Defining Hierarchical Website Structure
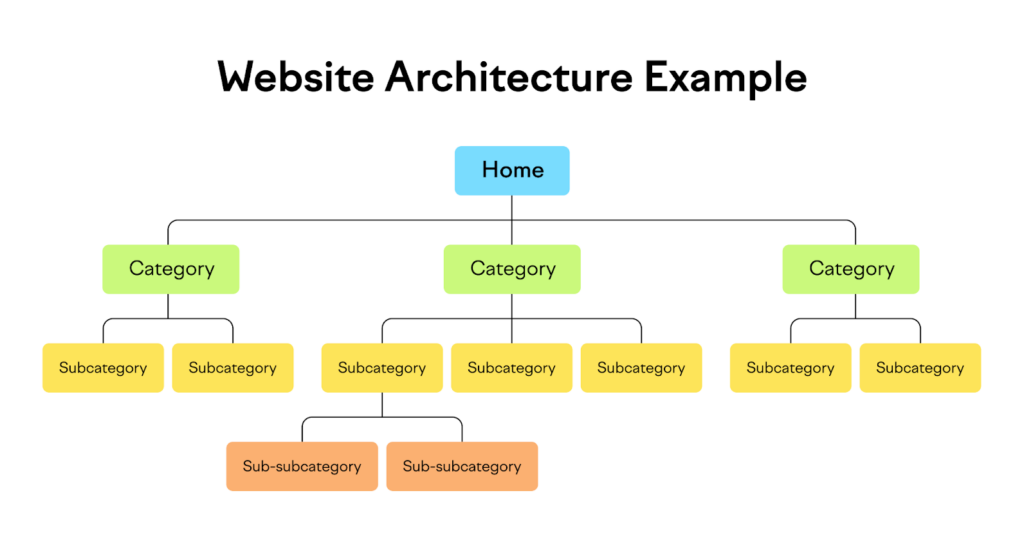
Hierarchical website structure organizes your content into a clear and logical pyramid. At the top is your homepage, which branches out to main categories, and under each category are subcategories and individual pages or posts. This pyramid should follow a 3-click rule, meaning any page should be reachable in no more than three clicks from the homepage, making everything easily accessible to both users and search engines.
The Importance of Navigation Menus
Navigation menus are one of the most important design elements as they guide visitors through your website. They should reflect the hierarchy of your site, showing the main categories at the top level and subcategories in dropdowns. Use descriptive labels in your menu to improve clarity, ensuring that visitors and search engines understand the content types on your site.
Header and Footer Elements
Headers and footers serve as key navigational elements. Your header should include your main navigation menu, making it easy to access from any page. Footers, on the other hand, provide a space for secondary navigation, contact information, and links to important pages like privacy policies or terms and conditions. Headers and footers contribute to a coherent structure that supports SEO.
Sitemap Essentials
A sitemap is a blueprint of your website that allows search engines to crawl it more efficiently. It should list all the important pages on your site, indicating the relationships between them. Both XML and HTML sitemaps are useful: XML sitemaps help search engines index your site, while HTML sitemaps are beneficial for users, enhancing navigation and overall site accessibility. It’s important to note here that pages which you do not need to be seen or indexed / crawled, should be excluded from the sitemap.
SEO and Website Architecture
Internal Linking and SEO-Friendly URLs
Internal linking enhances SEO by connecting your site’s content and guiding search engine crawlers and users through your site. A strategic approach to internal linking supports the distribution of page authority and rank power throughout the site. SEO-friendly URLs are clear, concise, and structured, incorporating keywords relevant to the page’s content.
Structured Data and Schema Markup
Implementing structured data and Schema markup in your HTML helps search engines understand the content and context of your pages. This can lead to rich snippets in search results, which may increase click-through rates. Use Schema to define articles, products, reviews, and more, enhancing the display of your pages in SERPs (Search Engine Result Pages).
The Impact of URLs in SEO
URLs are a fundamental element of SEO, and sometimes are a forgotten after thought during SEO optimizations. A well structured URL enhances user experience and search engine optimization efforts.
URL Structure and Site Hierarchy
Your website’s URL structure should closely mirror your site hierarchy, providing users and search engines with clarity on the relation between pages. Here’s why it matters:
- Navigation: A logical URL structure reflects a clear path through your website, making it easier for users to navigate.
- Clarity: URLs that accurately describe the page content improve readability for both users and search engines.
Consider a website’s nesting:
- Main category:
https://example.com/mens-clothing - Subcategory:
https://example.com/mens-clothing/shirts - Product page:
https://example.com/mens-clothing/shirts/casual-linen-shirt
This structure indicates a clear pathway from a broad category to a specific item.
Best Practices for Structuring URLs
When structuring your URLs, adhere to best practices that contribute not only to SEO but also to the user experience.
Include these elements:
- Keywords: Integrate 1-2 relevant keywords to clearly indicate page content. (although it’s confirmed that this doesn’t directly help with ranking, it does help the user’s intent and navigation)
- Simplicity: Keep URLs concise and avoid unnecessary parameters and characters.
- Readability: URLs should be easy to read and interpret by humans.
Avoid these pitfalls:
- Excessive use of stop words (like “and,” “or,” “but”).
- Overly lengthy and complex URLs with numerous subfolders.
- Frequent use of non-alphanumeric characters.